April’s smartKPI: % Hospital Bed Occupancy Rate

From over 20,600 Key Performance Indicators in our database, every month we select the most popular KPI and provide you with useful information about its calculation formula, benchmarking data, as well as on the best practices to maximize performance results. This month’s smartKPI is one of the most relevant metrics, utilized worldwide in measuring hospital performance.
KPI Description
One of the most searched for KPIs of all time on our website, % Hospital bed occupancy rate, is irreplaceable for effective hospital management, both in the private and public sector, regardless of geographical region or social aspects. Together with # Length of stay, this metric is used to assess the functionality degree of a hospital and the institution’s ability to efficiently manage its resources.
Definition
% Hospital bed occupancy rate measures the percentage of beds that are occupied by inpatients in relation to the total number of beds within the facility.
Sub-metrics
A = # Occupied hospital beds
B = # Beds within the facility
Calculation Formula: (A/B)*100.
For example, if a healthcare facility has 175 beds that are occupied by patients and holds a total of 200 beds, the occupancy is 87,5 %, having been calculated as (175/200)*100.
Limitations
A minor limitation of this KPI is that accurate reporting requires real-time registration of inpatients, so that no lag exists between actual hospitalization (and the occupancy of the beds), and registering it in the bed management system. However, most hospitals nowadays have an advanced health care management software, which ensures up to date inpatient records of admission and discharge.
KPI in Practice
Provided that the number of inpatients varies frequently, the data for this indicator should be captured on the spot and reported on a daily basis.
Regarding the ideal values for this month’s indicator, the result – calculated in the example above – 87,5% is optimal. Market data from our database, resulting from comprehensive global research on this KPI, indicates that 85-90% is the ideal range for % Hospital bed occupancy rate, as a rate higher than 90% may induce the danger of overcrowding, indicating that hospitals may have to turn away patients and postpone the provision of needed, possibly crucial, healthcare.
On the other hand, if results are below 85%, this might indicate that resources are managed inefficiently and inequitably. If results are between 70-85% respectively 90-95%, they are still within tolerance levels (and at the same time they represent a call to action), while values under 70% or over 95% can be regarded as reasons for concern (and corrective measures are to be taken immediately).
Benchmarking
Apart from the above-mentioned thresholds, benchmarking is also a paramount practice when working with our smartKPIs. This indicator should not be influenced by factors such as population density or geographical regions, since hospitals have to adjust to their local context so that they can fit the healthcare needs of their community.
However, factors such as seasonality or degree of economic development might still influence results. Thus, it is always recommended to benchmark against similar healthcare institutions in one’s geographical proximity.
Let’s analyze the graph below, published by the Ministry of Health Singapore. This graph compares the results of six major hospitals in the country: Changi General Hospital (CGH), Khoo Teck Puat Hospital (KTPH), National University Hospital (NUH) (Adults), Ng Teng Fong General Hospital (NTFGH), Singapore General Hospital (SGH), and Tan Tock Seng Hospital (TTSH).
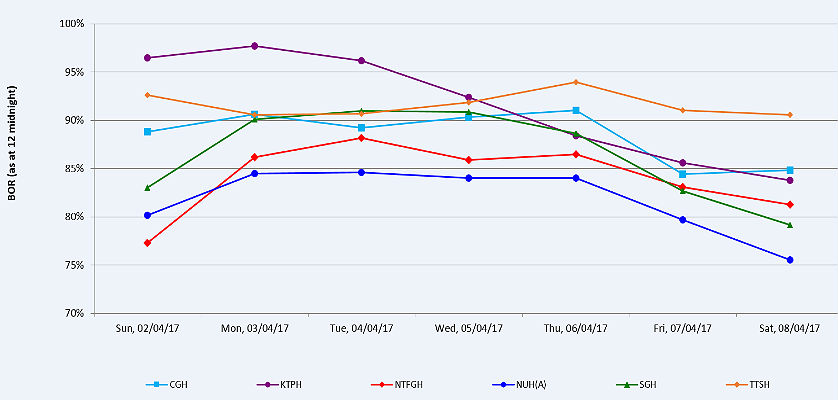
The % Hospital bed occupancy rate for the six facilities is measured on a daily basis, from Sunday to Saturday. The first aspect to be noticed is the ascending trend towards the middle of the week, when demand increases for most hospitals. Furthermore, for Khoo Teck Puat Hospital (KTPH) for example, values are dangerously high until Wednesday, reaching around 98% on Monday.
In Europe however, hospitals tend to stay on the safe side and keep their % Hospital bed occupancy rate mostly below 90%, as can be seen from a graph published by Eurostat.
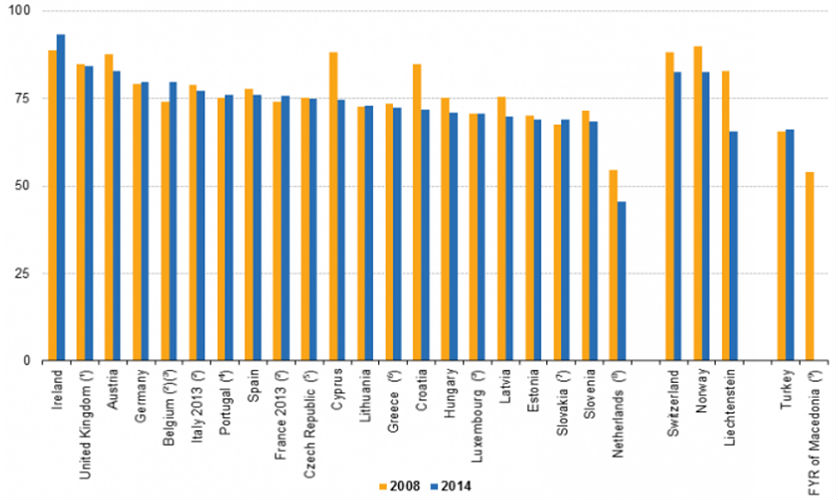
Two things must be noted here. Firstly, the graphs depict curative care bed occupancy rate. Secondly, it is important to mention that the various types of hospital beds can have uneven occupancy levels – curative care beds vs rehabilitative care, long-term care beds and other beds that are not included in these categories.
Key Performance Drivers
While hospitals should attune themselves from the start to local conditions in order to keep occupancy rates within range at all time, there are various uncontrollable factors which have to be considered in order to optimally employ this KPI. Thus, the following aspects should be considered:
- Medical specialties and their impact on bed occupancy rates (specialties like general surgery tend to have a higher bed utilization rate compared to ophthalmology, given the higher ratio of emergency admissions);
- Social and demographic characteristics of patients (teenage patients tend to have shorter lengths of hospitalization than patients above the age of sixty);
- Correlated services like medical treatment, diagnostic work, nursing care and so forth (since more intensive care usually requires longer hospitalization periods).
The effective use of available capacity is one of the criteria that most managers are especially concerned about. This parameter is of great importance since it can involve the loss of human lives. Very high occupancy rates, e.g. 98%, increase the danger of harm, including hospital-originated infections, while low rates – 40% – reflect an inefficient resource utilization.
Therein lies the importance of this month’s smartKPI, which should be monitored daily in order to ensure patient safety and satisfaction, and maintain an efficient & effective resource management process.
For a thorough analysis of your hospital performance, the % Hospital bed occupancy rate should be monitored together with closely related KPIs such as # Length of stay or # Hospital bed capacity.
Other related KPIs can be found in our latest Top 25 Hospitals KPIs – 2016 Extended Edition, one of the KPI Institute’s most popular publications. The report provides an overview of the most utilized KPIs in the Healthcare Industry, combining input from the smartKPIs.com community with research and analysis from The KPI Institute’s research team.
In May, we invite you to discover our next smartKPI, which is commonly used by Production Departments to measure and optimize performance!
Image sources:
- Pixabay
- Daily Bed Occupancy Rate (02 Apr 2017 – 08 Apr 2017)
- Curative care bed occupancy rate in hospitals, 2008 and 2014 (%)

Tags: Hospitals, KPI in Practice, SMART KPI, smartKPIs.com




justdial number gulbarga
| #
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites
Reply