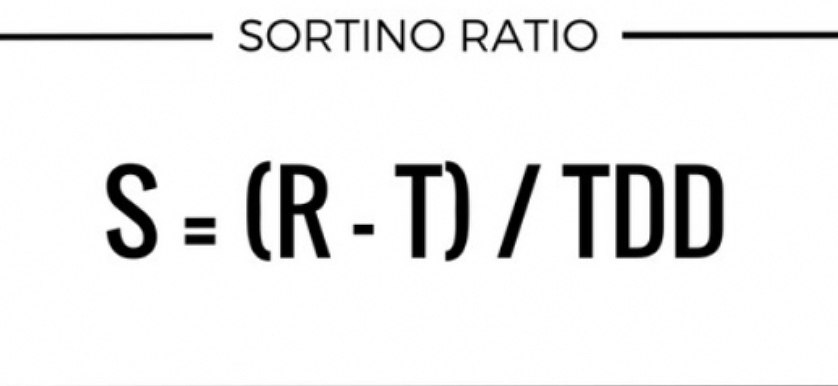
KPI of the Day – Investment: # Sortino ratio
Definition
Measures the risk-adjusted return of a security or fund’s performance, without penalizing it for upward price changes.
Purpose
To evaluate the actual rate of return in excess to the investor’s targeted rate of return, per unit of downside risk.
Recommendations
Investors, in general, desire to measure and compare not only the risks associated with the financial product they invest in, but also the gains they make through financial returns. Although the # Sharpe Ratio is commonly used in assessing the performance of products in the financial portfolio, by including potential losses into its calculation, the # Sortino ratio becomes more appealing to investors.
The Sortino ratio is a modification of the Sharpe ratio, but penalizes only those returns falling below a user-specified target, or required rate of return, while the Sharpe ratio penalizes both upside and downside volatility equally. Though, both ratios measure an investment’s risk-adjusted returns, they do so in significantly different ways that will frequently lead to differing conclusions as the true nature of the investment’s return-generating efficiency.
The # Sortino Ratio, as such, helps assess the investment not only from the perspective of the risk associated with it, but also from the perspective of its yield. Such thorough calculations are also useful when it comes to marketing products in the financial portfolio, forecasting future trends, as well as pricing for future business development strategies.
The # Sortino ratio can be measured in conjunction with the # Sharpe Ratio as well as the % Modified Sharpe Ratio to achieve a more accurate perspective on company results. Bear in mind, however, that when returns are nearly symmetrical, the indicators will produce similar results, and therefore it becomes useful to crosscheck in order to prevent errors.
Other recommendations to capitalize on the use of the # Sortino ratio in measuring performance are as follows:
- Observe the returns of the investment regularly to pinpoint any recurring patterns;
- Analyze the distribution of expected returns in order to have a full grasp on financial yields;
- Apply additional crosschecking calculations of the results to prevent errors and increase accuracy.
Image source:

Tags: Investments, KPI