Employee Engagement Index
In the last decade Employee Engagement has become a hot topic both in academic literature and in practice. The debate goes mostly around the implications that employee engagement can have on the success and bottom line of a company (Sacks, 2006).
It is widely known that organizations have traditionally relied on financial measures to determine their organizational value, success and financial performance through measures such as profitability, revenue or return on investment. It is also known that many soft measures or human oriented measures of traits, attitudes and behavior became in the last two decades more and more important determinants of employees and organizational performance (Peterson et al, 2001).
Many studies have shown the relationship that forms between employee cognitive attitudes, personality traits and job performance. However it was not clear until recently what is precisely the connection between all these components and how they can drive and determine organizational performance outcomes.
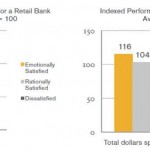
After 25 years of interviewing and surveying employees and managers the Gallup Organization has coined Employee Engagement Index as a driving force of the organization success and performance. (Little et al, 2006). The studies show that Employee Engagement Index has a significant implications for customer satisfaction, sustainable growth, real profit increase, stock increase, productivity and employee retention among the most important influenced factors (Gallup Consulting, 2008).
What is Employee Engagement?
Many academics and consultants tried to come with a definition of how employee engagement can be actually defined. Debates and research are still underway, but a common framework seems to emerge from the research work.
Many practitioners consider employee engagement a measure that reflects the extent to which employees contribute through their effort and enthusiasm to the success and performance of their organization.
In the same line of thought Crim et al (2006) consider that an engaged employee is a person inspired, fascinated, fully involved, and committed for its work and willing to see the organization succeeding in its mission. Accordingly, Sacks (2006) associates employee engagement with a sustainable workload, feelings of choice and control, recognition, fairness and justice, a supportive work community and meaningful and valued work.
How is Employee Engagement Index measured?
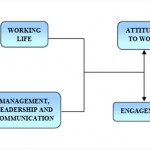
Employee Engaged Index is based on a survey questionnaire that assess the employees effort and enthusiasm at work and can vary from organization to organization. According with the researchers and consultants from Burke, a leading international research and consulting firm, there are 6 important engagement components that determine a substantive Employee Engagement Index:
• Company: satisfaction with the working environment and likeliness to withstand other job offers on the market
• Manager: satisfaction with the mangers
• Work group: satisfaction with the current working group: colleagues and managers
• The job: satisfaction with the job
• Career/ Profession : satisfaction with the choice of career and career perspectives
• Customer: Satisfaction with the working relationship had with customers/clients
Employee Engagement Index: Analysis and outcomes
According with the research studies underpinned by the Gallup Organization it appears that engaged employees are more productive, more customer focused and more likely to withstand temptations to leave the organization.
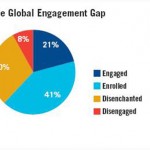
The same studies frame employees in three categories:
• engaged – work with passion and are profoundly connected to the organization values
• not engaged – put time but not passion in their work and they are not connected to the organizational values
• actively disengaged – employee busy to act out their unhappiness and undermine what their engaged colleagues try to accomplish ( Crim et al, 2006)
Based on these categories Gallup built the Engagement ratio which according with them is a macro level indicator that allows organizations to track the ratio of engaged to actively disengaged employees.
The results show that:
• In average the ratio of engaged to actively disengaged employees is 1,5 to 1
• In world class organization (successful organizations) the ratio of engaged to actively disengaged employees is 8 to 1
This difference between the engagement ratio for average and world class organizations is translated in the way a suite of performance indicators are affected by employee engagement and how in the end they affect consequently the bottom line of the organization. (see graph below, Gallup – Employee Engagement)
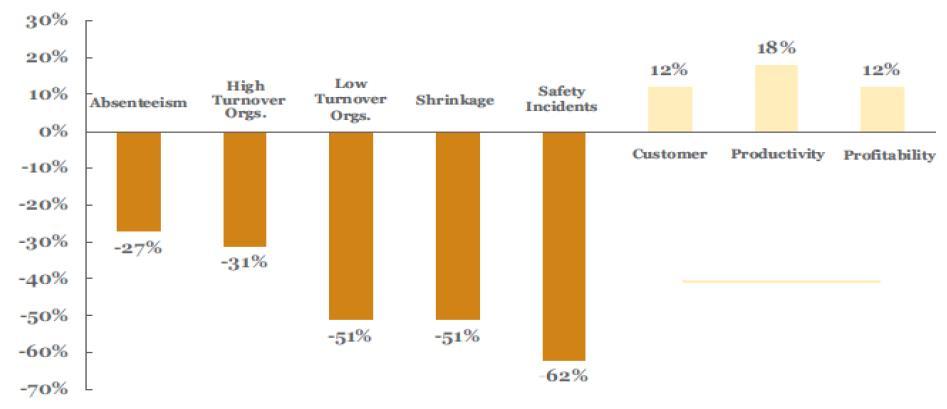
As we have seen above employee engagement has a direct influence on a series of other performance measures which in the end consequently determine and drive the performance outcome of an organization. In this context, as the Gallup researchers acknowledge, for successful organizations the Employee Engagement Index transcends from a human resource initiative, “into a strategic approach supported by tactics for driving improvement and organizational change”
For more resources and information on human resource management please visit our performance measures and KPIs database on smartkpis.com.
References:
- Sacks, M. Allen (2006): Antecedents and consequence of employee engagement, Journal of Managerial Psychology, Vol 21, No 7, pp 606-619
- Peterson, J. Suzanne and Luthans, Fred (2002): Implications for managerial effectiveness and development, Journal of Management Development, Vol 21, No 5, pp 376-387
- Crim, Dan and Seijts, H. Gerrard (2006): What engages employees the most or, The ten C’s of employee engagement, Ivey Business Journal, March/April
- Little, Beverly and Little, Philip (2006): Employee engagement: Conceptual issues, Journal of Organizational Culture, Communication and Conflict, Vol 10, No 1, pp 111-120
- Burke Consulting, Employee Engagement and Retention Management
- Gallup Consulting (2008), Employee Engagement: What’s your engagement ratio?

Tags: Human Resources performance, Performance Measurement