Sustainability Standards and KPIs as Game Changers

Image source: Kiefer Likens | Unsplash
Companies can no longer afford to ignore sustainability. It is not just a trend but a major factor that drives where most businesses are headed. According to Globescan’s The State of Sustainable Business 2019, reputational risks, consumer demand, investor interest, operational risk, and employee engagement are some of the catalysts behind the sustainability efforts of most organizations.
Manufacturing is one of the industries that are pressured to realign their activities with the mounting call for sustainability practices. Sustainable manufacturing refers to developing products with minimal negative environmental impacts and maximum contribution to the conservation of natural resources. These products are expected to be economically sound and safe for employees, communities, and consumers.
Sustainable manufacturing aims to reduce the intensity of materials use, energy consumption, emissions, and unwanted byproducts while maintaining or improving the value provided for society and organizations.
Some relevant key performance indicators that are often considered when evaluating the sustainability of manufacturing companies are:
- Environmental performance KPIs, such as: # Air emissions, % Energy utilization, % Hazardous waste etc.
- Economic performance KPIs: % Product reliability, % Conformance to specifications, $ Material cost, % Labor cost etc.
- Social performance KPIs: % Occupational health and safety, % Turnover rate, % Supplier commitment etc.
Sustainability standards are observed to ensure quality, transparency, compliance, and results in terms of making organizations accountable for their economic, environmental, and social performance.
Read More >> Everything You Need to Know about KPI Selection
The GRI Standards
Among the internationally renowned frameworks is the Global Reporting Initiative’s (GRI) Sustainability Reporting Standards. The GRI Standards consist of Universal Standards, which apply to all organizations and report on human rights and environmental due diligence, the new Sector Standards for sector-specific impacts, and the Topic Standards that come with the revised Universal Standards and relate to a particular topic.
Their visionis to create a sustainable future enabled by transparency and open dialogue about impacts. In this regard, they are a provider of the world’s most widely used sustainability disclosure standards.
With GRI Standards, companies can publicly present the outcomes of their activities in a structured way. This allows their stakeholders and interested parties to better see their status of how they are responding to calls for sustainability. GRI Standards can be used by any type of organization, whether large or small, public or private, or from any location or industry.
As cited in the report “A Short Introduction to the GRI Standards,” the Reporting Process for organizations using the GRI Standards involves determining impacts and their significance, identifying material topics, or topics that are relevant to the organization’s activities, and reporting disclosures. The final stages are reporting the organization’s most significant impacts on the economy, environment, and people and publishing information and GRI content index.
The GRI Standards comprise three series of Standards: The GRI Universal Standards can be applied to your reporting. The GRI Sector Standards are for sectors while the GRI Topic Standards are used to report specific information regarding material topics.
Daimler’s Sustainability Report
An example of a sustainability report that is developed based on the GRI Standards comes from Daimler, one of the biggest producers of premium cars and the world’s biggest manufacturer of commercial vehicles.
In 2006, Daimler joined the multi-stakeholder network of the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), where it initially was an organizational stakeholder. It later became a Gold Community Member and is now a member of the GRI Community.
Their report is based on the Daimler Group’s sustainable business strategies. It contains two conceptual levels: “Spurwechsel” section, which refers to the external sustainability developments and trends into a context with the internal strategies and measures and “Reporting” section which provides a detailed description of the goals, due diligence approach, measures, and achievements.
The Reporting section focuses on six areas of action: climate protection and air quality, resource conservation, livable cities, traffic safety, data responsibility, and human rights as well as on three enabler topics, which are cross-sector themes that can influence areas of action. The enabler topics are Integrity, People, and Partnerships.
As part of the Climate protection & air quality area of action, the manufacturer frequently monitors the compliance with the internal and external environmental protection requirements. This way, they can take proactive actions to eliminate possible damage.
As a result, the reduction of air emissions is an important focus of their sense of responsibility for the environment (Figure 1).
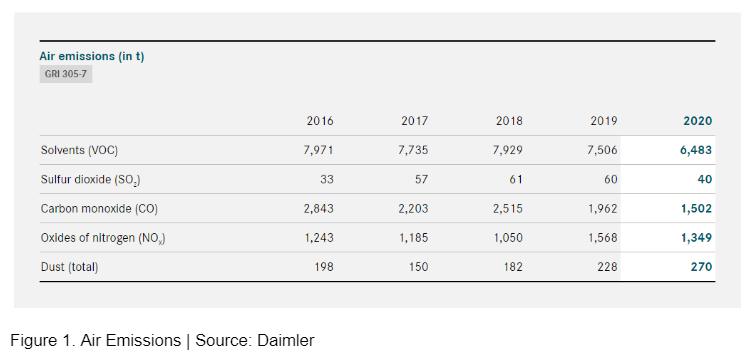
They consider the consumption of resources in production as an important factor in the environmental compatibility of their vehicles. Thus, they are working to make production more efficient and more environmentally friendly by using less water, energy, and raw materials.
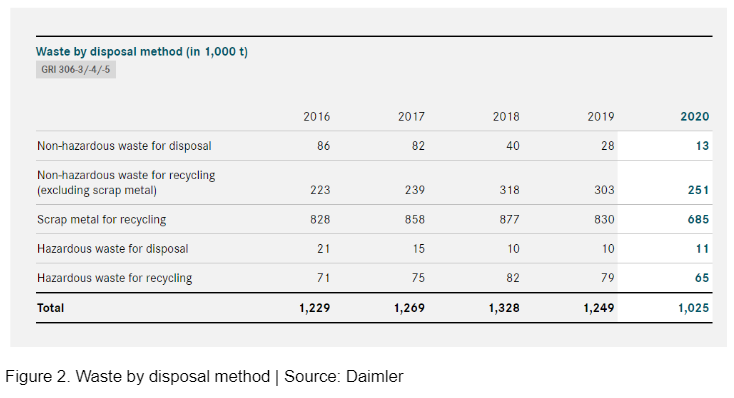
Daimler evaluates in a consistent and transparent way the economic, environmental, and social impact in order to find the best solutions to remain climate-neutral and sustainable in the future.
In addition to this, they maintain regular contact with representatives of business, government, and other interest groups that advocate for the same goal.Daimler also plays an active role in upholding the UN Global Compact, a voluntary initiative that encourages companies to integrate sustainability practices into their activities. Daimler shares on their website that they are involved in the thematic and regional working groups and initiatives of the pact.
“In the reporting year, these included the action platforms “Reporting on the SDGs” and “Decent Work in Global Supply Chains” as well as the UN Global Compact Expert Network and the German Global Compact Network,” Daimler states.
Read More >> Ask Our Experts: Principles on Creating Meaningful Sustainability Reports
As part of its obligation, Daimler reports its initiatives on areas like human rights, labor standards, and environmental protection in its Sustainability Report
Reporting sustainability key performance indicators constantly, in a clear and transparent manner, can provide a clear overview of the environmental, social, and economic impacts, and based on this, the organizations can take proactive actions to reduce the negative impact.
In this context, The GRI Standards offer a consistent structure for companies to report information in a way that covers the most significant impacts on the economy, environment, and people.
To learn more about KPIs, visit the world’s largest database of documented KPIs: smartkpis.com.**********
Editor’s Note: This article originally appeared in the 22nd edition of the Performance Magazine Printed Edition and was published online on February 22, 2023. It is last updated on September 17, 2024.



