Bermuda – on the path of becoming a leader in Government effectiveness

Governing effectiveness is the foundation of a country’s state development and it triggers progress in all key areas: security, economic and social context, as well as environmental matters.
As it is quite a complex phenomenon, governing performance can be measured through several performance indicators or indices. Based on The KPI Institute’s indices taxonomy, one significant index for measuring state administration performance is the # Government Effectiveness Index. The index, created by The World Bank, measures the opinion of enterprises, citizens and experts regarding the effectiveness of quality, gathering data from survey institutes, think tanks, NGOs, international organizations or the private sector.
Hence, it is based on the wider public’s perception of the government’s ability to deliver quality services, its capacity to effectively formulate and implement national policies, the government’s credibility and the trust citizens bear in the institutions that govern their economic and social interactions. The score of the # Government Effectiveness Index has values between -2.5, expressing the smallest level of effectiveness, and 2.5, indicating the strongest level of effectiveness.
In its composition, the index includes 6 major inquiry areas or sub-indices:
- Control of Corruption;
- Government Effectiveness;
- Political Stability and Absence of Violence;
- Regulatory Quality;
- Rule of Law;
- Voice and Accountability.
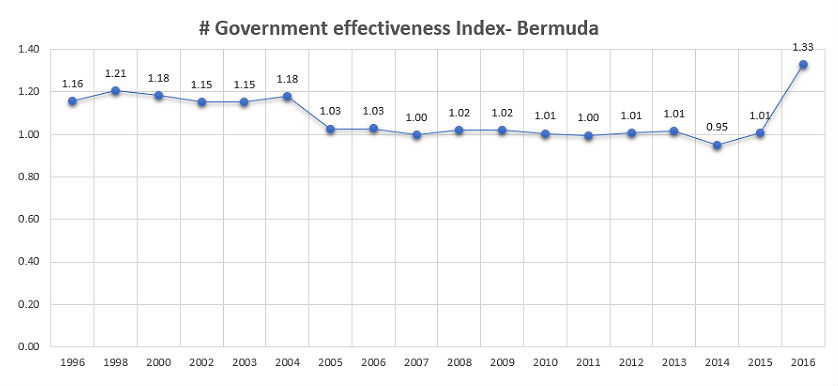
In the past 20 years, Bermuda has been constantly scoring between 1 and 1.33. Taking into consideration the range of values that the # Government Effectiveness index allows, Bermuda’s scores can be considered a country with a moderate-to-strong level of effectiveness, with a percentile rank of 87.98 out of 100 in 2016 and a percentile rank higher than 75 based on the historical data.
However, lately there has been increased awareness in Bermuda regarding the need to develop sound efficiency programs for the public sector that go beyond timeliness and focus on performance standards.
This reform has started in 2008 by appointing an independent body to audit and make recommendations for change and is now continued through the Ministry of the Cabinet Office with Responsibility for Government Reform. The Ministry is working on a framework of accountability, collaboration, transparency, and integrity, which can be correlated with important aspects measured by # Government Effectiveness Index, such as Accountability or Control of Corruption.
Another important part of the reform taking place in the country refers to the Rule of Law, with Bermuda’s Minister of the Cabinet Office with Responsibility For Government Reform stating that “empowering the Legislature to have a more robust role” is required in order to have a successful reformation of the government and to further increase its efficiency. Such measures are also aimed at reducing bureaucracy, which fosters efficiency.
Thirdly, the Ministry has planned the implementation of three permanent Parliamentary Oversight Committees “in order to improve governance, reduce waste and increase efficiency”, with the specific task of holding the Government accountable and ensuring transparency. Their efforts have become so noteworthy, the country has even won an international recognition for transparency from the EU and the USA.
Lastly, the fight against corruption is supported by the United Nations Convention Against Corruption and the OECD Convention on Combating Bribery of Foreign Public Officials in International Business Transactions, both of which are sought to be extended, in order to further strengthen Bermuda’s status as an exceptional offshore financial centre.
All in all, although the country only has a medium-to-strong level of government effectiveness, it is on the path to improve its performance at this level, and there are at least three key learning points that other governments can take from Bermuda’s example, which can help them increase their efficiency based on more than just service time:
- Setting a performance management system based on a clear framework which fosters accountability, collaboration, transparency and integrity;
- Establishing clear requirements as part of the regulations;
- Establishing quality or control bodies to make sure their performance management system is implemented correctly.
Image sources:

Tags: Government performance, World Bank