Bahrain’s First Voluntary National Review Report on Sustainability

The Kingdom of Bahrain has taken ownership for inclusive sustainable development, by adopting the UNDP’s 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), aimed at “ending poverty, protecting the planet and ensuring that all people enjoy peace and prosperity”.

78% of the 2030 SDG objectives were linked to the Government Action Plan, establishing primary and secondary goals for each strategic priority and overarching theme, thus synchronizing the national agenda with the UNDP ‘s international efforts. These are the following:
1. Sovereignty
Strategic priority: Promote security and stability, the democratic system and Foreign Relations
For this particular priority, focus will be mainly on peace-building, strengthening the justice system and its related institutions.
2. The economy and finances
Strategic priority: Nurture a strong and diversified economy, and a stable financial & monetary system
This priority will focus on ensuring jobs are in a healthy & diverse state, as well as readily available, so that the country’s economic growth can continue, and its dependence on oil lessen.
In 2017, a non-oil growth of 5% allowed Bahrain to become the GCC’s fastest growing economy for that year.
3. Human development and social services
Strategic priority: Empower Bahrainis to raise their contribution to the development process
This will entail working on three different, however nonetheless related objectives: poverty, healthcare and education. Bahrain already has made outstanding strides for the first one, ensuring no soul lives in absolute poverty.
Education has also seen great forward strides, with virtually a complete attendance in primary school of all children that are of the required age.
Healthcare is however still a slight struggle, as Bahrain is currently experiencing an escalating rate of NCDs – Non-Communicable Diseases. The biggest causes for concerns are diseases related to the circulatory system, representing 34% out of total deaths caused by NCDs. Diabetes (24%) and Cancer (15%) are the two biggest secondary ones, with several other NCDs amounting to the rest of 27%.
Moreover, this struggle is exacerbated by the way healthcare is financed, as there are limited avenues for the private market to chip in and help. Thus, Bahrain is looking to open up new gateways, with one such initiative being the implementation of private health insurances, in order to spur citizen choice and decrease the economic burden on the state.
4. Infrastructure
Strategic priority: Secure infrastructure to support sustainable development
The biggest focus for this priority is ensuring clean water and sanitation. Bahrain was listed among the top 10 countries that are the most likely to suffer from a water crisis in the next 25 years in a report released by the World Resources Institute.
Water quality in Bahrain is affected by the extremely high salinity of its accessible water. In 2008, AQUASTAT, a program measuring water quality within the U.N. Food and Agricultural Organization, reported that “over-utilization of the Dammam aquifer, the principal aquifer in Bahrain, by the agricultural and domestic sectors has led to its salinization through water coming from adjacent brackish and saline water bodies.”
One solution was the creation of water storage facilities throughout the country, a few years ago. As a large part of its water security system, storage tanks of potable water were used to ensure supply during crisis situations. In 2013, the storage tanks held a water capacity that could ensure the survival of the nation for two days in case of extreme emergency conditions, leading to improvement of water quality in Bahrain.
5. Environment and urban development
Strategic priority: Sustainable management of strategic resources and insuring sustainable urban development
This priority once again focuses on ensuring sanitation & clean water, building upon the previous one’s achievements; however, it also includes generating affordable and clean energy, as well as building sustainable cities and communities.
6. Effective governance
Strategic priority: Enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of government performance
Given the complexity of Bahrain’s decision-making system, with the state playing the largest role in all areas, it has become increasingly necessary to streamline its processes across all ministries and departments.
Moreover, the country’s government will look to create logical, direct links between ministry projects, in order to have an easier time following through with any of its localized action plans.
Between 9-18 July, the country disseminated its key achievements at the Voluntary National Review of the High-level Political Forum. The most important accomplishments include:
- No poverty: in Bahrain, the average income for families increased by 47% in 10 years and no one in the country suffers from hunger or malnutrition, according to the Voluntary National Review Report on the SDGS;
- Quality education: Bahrain has improved enrollments to primary school (100%) and secondary school (86,4%);
- Gender equality: 55% of Bahraini women are now in supervisory positions, while 53% participate in the public sector and 33% in the private sector. According to the report, 15% of the seats in the national parliament and local governments are held by women;
- Decent work and economic growth: Bahrain’s GDP grew by 3.9% and its non-oil economy by 4.7% in 2017. On top of that, the country’s unemployment rate is stabilized at 4.3%;
- Sustainable cities and communities: five sustainable cities are being developed in the country and 65% of the population benefitted from public housing
- Clean water and sanitation: the coverage of safe water and clean energy networks reached 100%;
- Affordable and clean energy: 100% of the population has access to electricity and relies primarily on clean fuels and technologies.
To monitor the implementation process, the government set 232 indicators for the 17 sustainable development goals, and their 169 specific objectives.
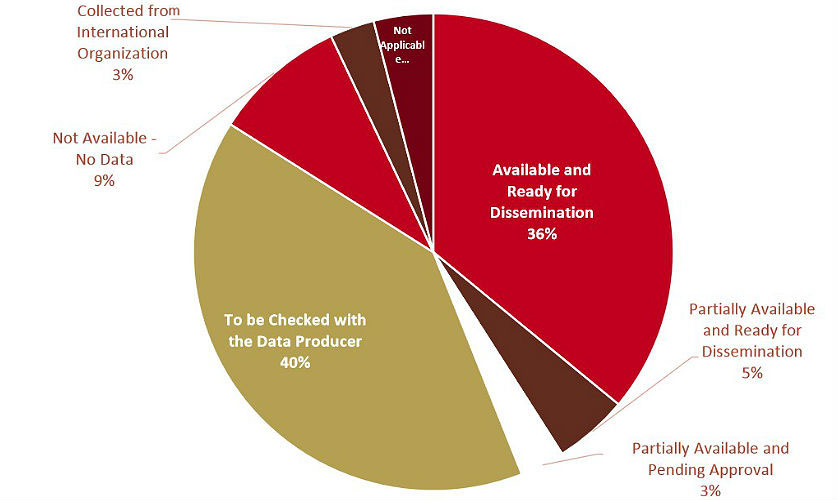
The latest report of the Information and eGovernment Authority specifies that 36% of the indicators are available and ready for dissemination, 40% are yet to be checked with the Data Producer, while 9% of the indicators don’t have the relevant data available.
All of this being said, despite the great progress made last year, the government faced some key challenges during the initial stages of the implementation, such as achieving high economic growth rate while maintaining price stability or providing the necessary funding for sustainable production and green technologies. In addition to this, it lacked an appropriate response to addressing extremism and terrorism.
As data is becoming more and more available, Bahrain will need to decide what it should work on first – fixing current challenges or further improving those areas that have already experienced good results.
Image sources:

Tags: Government performance, Performance in Bahrain, Sustainability performance




