Advice on KPI selection
KPI selection is a process which seems simple, yet is inherently complex, due to the interdependencies involved. Here are 15 things to consider before embarking on this journey.
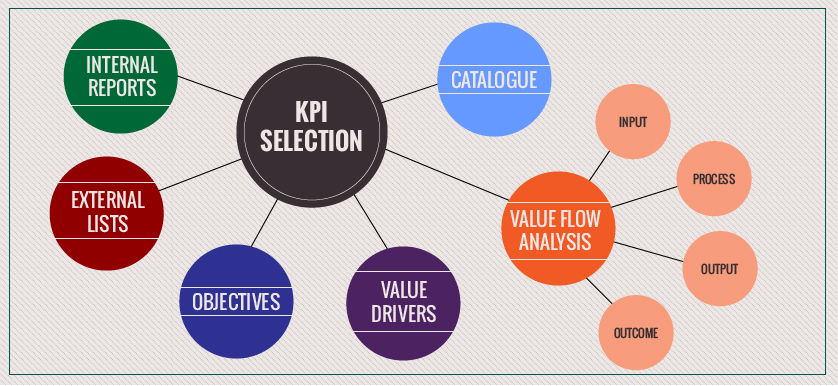
1. Review existing internal reports and support documents at the beginning of the KPI selection exercise. These may include previous business/strategy plans, annual reports, performance reports and other documentation that relates to performance management, measurement and benchmarking.
2. Use external lists of examples and other secondary documentation to inform and support KPI selection. It is always a good idea to begin a journey having the end in mind. Reviewing KPI examples used in the industry or functional area, by competitors or other organizations provides context around what is in used in practice by others and improves understanding around the desired output.
3. Engage internal stakeholders in the process of KPI selection through interactive workshops. KPI selection is not a desk exercise. It is an opportunity to communicate and learn, hence an open discussion in a workshop format is a better approach for enabling not only KPI selection, but also understanding and ownership.
4. Calibrate KPI selection around business objectives and value drivers. KPIs are not used in isolation. They are just one component of the value creation chain and of the performance management system. A simple way to position them is al links between business objectives and related organizational initiatives.
5. Select KPIs based on the realities of organizational activity and environment. Each organization is different, operating in different environments, with different guiding principles. Hence the KPIs used need to reflect the specifics of each organization first and industry/functional area characteristics second.
6. Maintain a centralized catalogue of KPIs for the entire organization. Structuring KPI documentation in a central repository facilitates their understanding and usage in a similar way across the organization, growing the know-how and facilitating KPI selection and usage on an ongoing basis.

7. Understand the difference between input, process, output and outcome KPIs. This value creation sequence is essential in facilitating the understanding of KPIs in the context of the value added by the process/activity they are related to. It is an essential mapping technique that facilitates KPI selection.
8. Don’t hesitate in changing KPIs in scorecards and dashboards. KPIs should reflect activity and activity should adapt to a changing environment. The use of KPIs should be fluid and flexible, reflecting the change in business priorities as a result of the change in the operating environment.
9. Review KPI relevance regularly. If new KPIs are required, they can be established at any time. An essential aspect of double loop learning. Using KPIs is not only about achieving set targets and objectives, but also about ensuring the objectives and targets were the right ones to be set in the first place and the KPIs used to track their achievement were the appropriate ones.
10. KPI selection and target setting should be done in accordance with organizational maturity and direction. There is no one size fits all approach when it comes to using KPIs. As strategies vary from one organization to another, the use of KPIs also varies.
11. Project milestones are not KPIs. Understanding the difference between what is and what is not a KPI is a prerequisite of successful KPI selection.
12. Targets are not KPIs. Understanding the anatomy of a KPI is essential in KPI selection and usage.
13. Some things are not worth measuring. For example measuring love might not be such a good idea. Not everything that can be measured should be measured with KPIs.
14. Some things are too difficult to measure. For example cuteness. The “measuring everything that moves’ mentality should be avoided.
15. Eliminate or replace inactive KPIs with simpler, yet measurable ones. Using some KPIs may have seemed a good idea at the time of their selection, however if measuring them proves to be too costly or time consuming, they should be replaced. An active KPI is better than an inactive KPI.
If you are interested in learning more about KPIs, smartKPIs.com subscriptions provide access to +500 KPI examples. Our dedicated Library contains relevant resources to improve your KPI practices, and if you want to further improve your knowledge, feel free to explore any of our latest publications at marketplace.kpiinstitute.org.
Image source:

Tags: KPI, KPI Selection