Performance Benchmarking in the Gas Utilities Sector

The KPI Institute’s “Key Performance Indicators for Gas Utilities” report is part of the extensive secondary benchmarking launched back in 2016/2017, through our Center for Performance Benchmarking and Utilities Performance Labs. The report includes data from 23 gas companies, located in 17 countries, situated on 5 continents, in order to provide worldwide coverage and enable better comparison between companies, as a benchmarking process in the case of gas utilities can be influenced by the geographical regions.
Knowing how to better position on the market and assess performance levels in comparison to competitors was always of interest for companies as it enables them to come up with improvement initiatives and reach or surpass the industry’s standards. Following the needs of the companies, this benchmarking initiative was launched.
The 166 key performance indicators included in the report were structured into a comprehensive framework consisting of 5 clusters further divided in sub-clusters. The KPIs contained by the report were selected based on the frequency of reporting them among the companies analyzed, although some KPIs were included as a recommendation of the professionals within The KPI Institute.
A) The first cluster, Customers is focused on Market Distribution and Account Management and reflects on the interaction between the organizations and their clients. Based on the analysis conducted we have noticed 4 KPIs which are essential for gas organizations:
- # Operated residential customers;
- # Industrial customers;
- # Customers per agent;
- # Total utility accounts.
B) The Operations cluster includes 32 KPIs, which aims at reflecting on the performance of production and distribution system, but also on the reliability and quality of the infrastructure, considering that aging infrastructure is one of the main challenges gas utilities companies face. Out of the 32 KPIs, we recommend professionals to give a special attention to the production per type of gas, such as:
Other lead KPIs we recommend professionals to measure would be:
- % Thermal efficiency;
- # Capacity of underground gas storage facilities (billion m3);
- # Breakdown of gas supply.
C) The third cluster, Environmental Impact, is highly emphasized by gas utilities when reporting their performance as it encompasses 41 KPIs, which is understandable given the amount of external regulations and pressure put on reducing the environmental footprint. The gas utilities included in the report KPIs which have to do with:
- Green Gas Emissions (# Nox, # Sox, # Non-methane volatile organic compounds);
- Spills Management (# Spills, # Operational spills, # Sabotage spills);
- Waste Management (# Hazardous waste, # Total waste, # Compost).
D) The Corporate Governance cluster is, more or less, overlooked when measuring and reporting performance within the gas utilities sector. Only 3 key performance indicators were considered relevant for the benchmarking study and the companies reckoned to measure the efficiency of Corporate Governance are Shell Energy North America and GDF Suez, which look at:
E) The Human Capital KPIs group is by far the one in the spotlight for gas utilities, comprising 86 out of the total of 166 key performance indicators and is further divided in several sub-clusters:
- Workforce profile, focused on showcasing KPIs which measure the age and employees’ distribution between different departments of the company. For this sub-cluster, our recommendation is to focus on staff distribution, as it can be used as a leading KPI for staff distribution optimization.
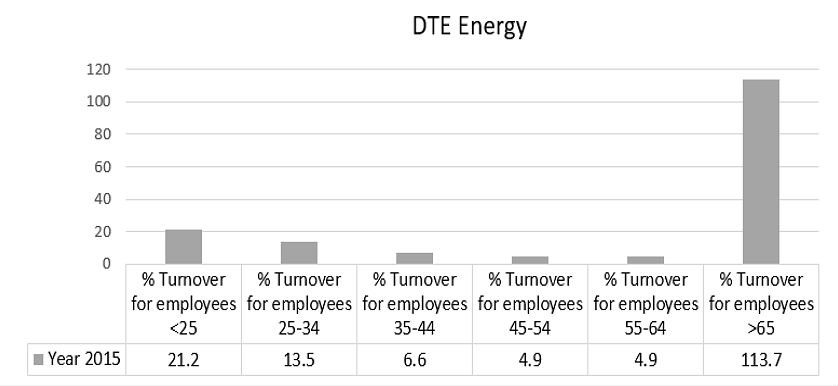
- Turnover, which pinpoints to different ways of expressing the KPIs measuring turnover. An example can be measuring % Turnover at departmental levels or age gap, as shown in the graph below.
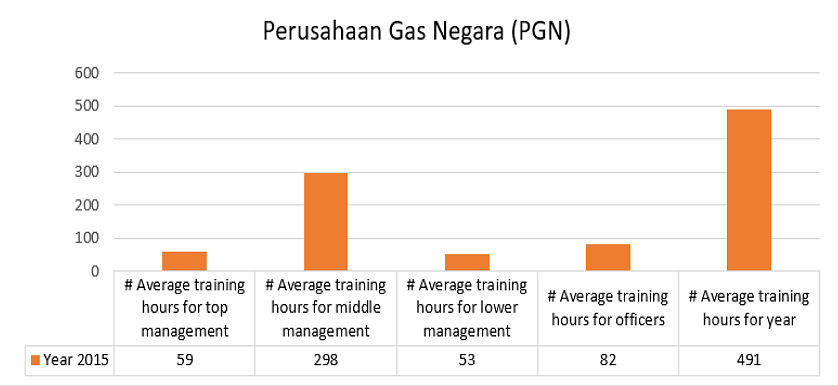
- Professional development is centered around continuous staff development and training. The KPI Institute’s suggestion is to measure the # Average number of training hours per department or hierarchical level, as represented below.
- Innovation, measuring the number of patents, whether as a total or breakdown per department/type, is important for every company, and gas utilities can benefit and become more competitive.
- Health and safety is an important issue for gas utilities given the risky environment their staff operates in, hence measuring KPIs such as % Accidents frequency rate, % Fatal accidents, # Total days lost due to accidents is imperative in order assure a safety working environment.
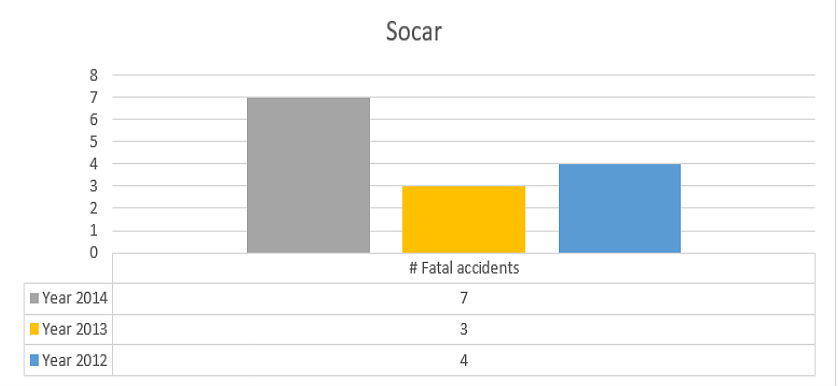
Taking into consideration the recommendations above, we can draw some simple conclusions and tips:
- Gas utilities need to take into consideration their external system when reporting performance as regulations or the geographical conditions can affect what they have to report or their performance;
- When choosing the KPIs to be measured for each cluster, gas utilities need to take into considerations the strategic objectives and their needs, no just what is measured within the sector;
- Professionals within gas utilities have to remember that the five clusters are interconnected and performance levels in one cluster can be influenced by the levels of performance measured by KPIs from other clusters. Hence, all the KPIs chosen should be interconnected and follow the strategic objectives.
Image source:

Tags: Key Performance Indicators, KPI, Oil and Gas performance, Report Analysis




