Blockchain – The Future of Transactions

Economic, legal and political systems are constructed and held together by contracts and transactions. They are vital tools that protect assets and set organizational boundaries, that control interactions between nations, organizations and individuals, and that guide managerial and social action. But despite their crucial role, these tools are not up to date with the economy’s digital transformation.
Blockchain is the technology that stands at the center of bitcoin and other virtual currencies. This technology is a ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way. The ledger itself can also be programmed to trigger transactions automatically. This technology promises a very different and innovative future in transactions.
How does Blockchain work?
- Distributed Database – each party on a Blockchain has access to the entire database and its complete history. No single party controls the data or the information. Every party can verify the records of its transaction partners directly, without an intermediary.
- Peer-to-Peer Transmission – peers communicate directly and not through a central node. Each node forwards information to every other node.
- Transparency with Pseudonymity – transactions are visible to anyone that has access to the system. Each user on a blockchain has a unique 30-plus-character alphanumeric address that identifies it. Users can choose to remain anonymous or provide proof of their identity to others.
- Irreversibility of Records – once a transaction is entered in the database and the accounts are updated, the records cannot be modified, because they’re linked to every transaction record that came before them.
- Computational Logic – the digital nature of the ledger means that Blockchain transactions can be tied to computational logic and programmed. Users can set up algorithms and rules that automatically trigger transactions between nodes.
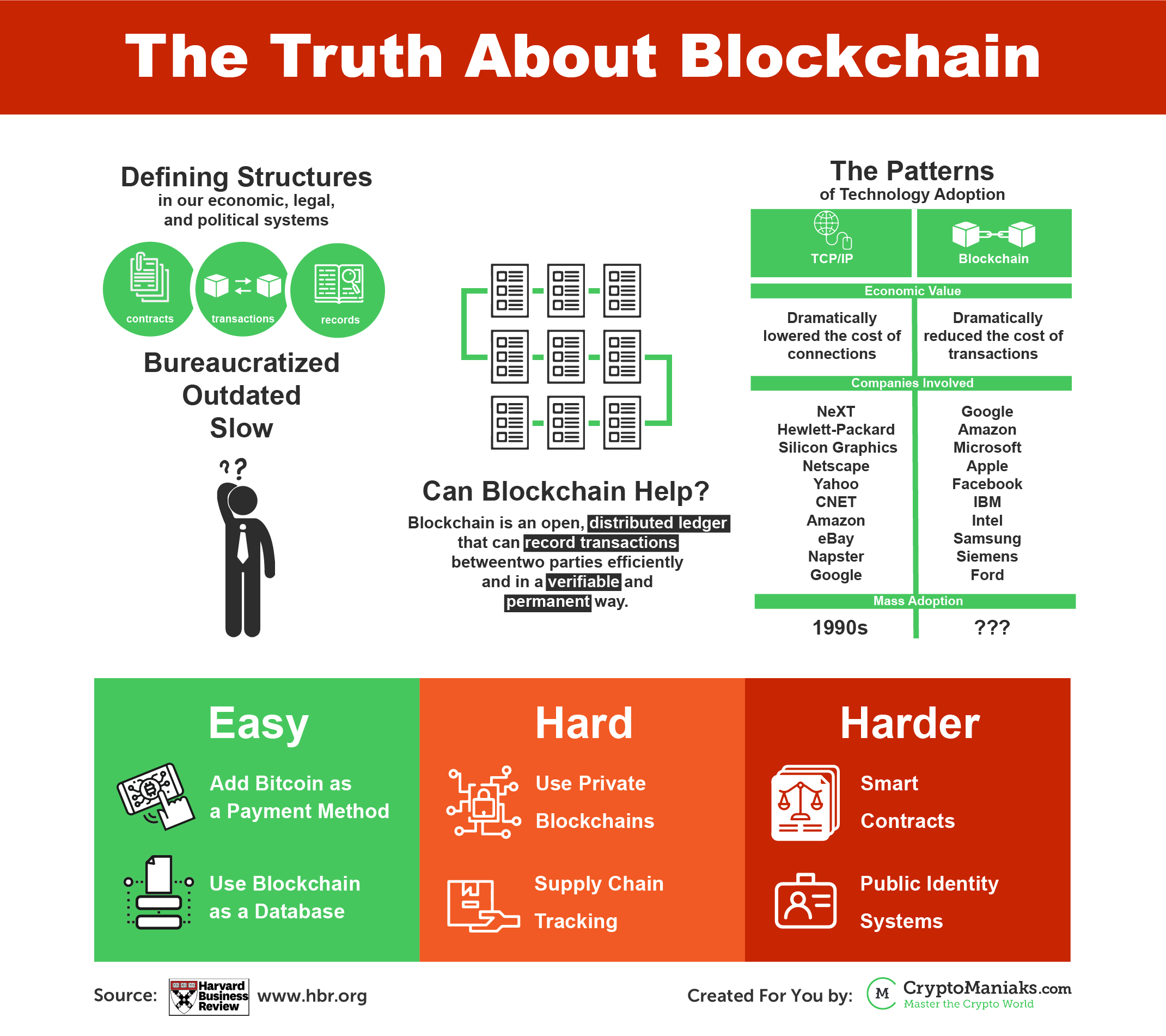
A world that has Blockchain in it is a world in which contracts are enclosed in digital code and stored in transparent, shared databases, where they are protected from deletion, tampering and revision.
In the Blockchain world we won’t need lawyers, bankers and brokers, and both individuals and organizations will interact easier and with less friction.
Although Blockchain has an immense potential, it is nonetheless a foundational technology. This means that it can create new foundations for the economic and social systems of today, but the process can last for decades. It will be gradual and its integration will take time. The only question is when.
Image source:
Tags: operational performance, Technology, Tools