How to build a strategy map and increase business performance
By identifying what differentiates it from its competitors, as well as by acknowledging its main capabilities, an organization can set the objectives that have to be attained in order to reach its vision. A performance-focused organization will formulate its objectives and map its strategy, in order to identify cause and effect links that turn assets into desired outcomes.
Objectives are clearly defined statements of what an organization sets out to achieve. They are important strategy components which reflect on strategic priorities and the overall strategic plan.
Objectives embody the link between the mission/vision of the organization and its related initiatives/activities. Clarifying objectives serves for performance monitoring and evaluation, while providing the necessary framework in aligning organizational priorities.
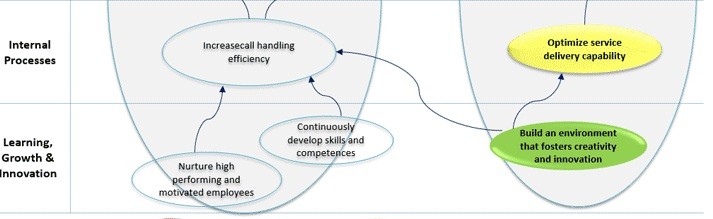
The Strategy Map is a visual representation of an organization’s strategy, highlighting the strategic objectives of the organization and the cause and effect relationships, linked within the four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard.
The Strategy Map components are:
- The strategic objectives, structured within graphic representation models, such as ovals, which can be adequately colored, according to target thresholds:
- Red: Bellow targets (Unacceptable values)
- Yellow: Within target limits (Acceptable values)
- Green: On or above targets (Desired values)
- The Balanced Scorecard Perspectives, horizontally grouping strategic objectives within each perspective, as reflected by the Strategy Map;
- The cause and effect relationships visually represented by arrows linking strategic objectives both horizontally and vertically
- Strategic themes, which establish the required criteria used to group together strategic objectives within the Balanced Scorecard perspectives of the Strategy Map.
The organizational Strategy Map is a performance management tool that:
- Provides and architecture for describing the strategy;
- Maps the organization’s strategic objectives and uses a cause and effect logic to reflect their interdependencies;
- Helps executives turn strategy into outcomes by providing a framework for the process;
- Groups strategies into relevant themes for optimal segmentation and execution;
- Makes strategy operational at all levels of an organization by effectively communicating strategy and related objectives.
There are several best practices that need to be taken into consideration when designing a Strategy Map:
- Choose the right template
When building a Strategy Map, the template must provide a structure that clearly illustrates an organization’s strategic objectives, initiatives and targets, while emphasizing the connections between objectives and themes that aim for the same strategic direction.
Strategy Maps may all be based on the same guidelines, but choosing the right visual outline is a decision of how the Strategy Map template best suits the company’s vision on performance.
- Start from the top down
The optimal way to build a Strategy Map is starting with the vision of what an organizations wants to achieve, and then identifying the actions required to get there. A company must first envision its purpose and then develop a strategic vision.
- Identify what’s missing
Strategy Maps can help identify flaws in the way the strategy is implemented at different levels of the organization. It is important for business units to be aligned with company strategy. Performance measurement should not be eluded at lower levels of the organizations, and strategy maps are a good tracker of such omissions.
- Adjust to best reflect the strategy
When missing pieces in strategy execution are identified by the use of a Strategy Map, adjustments are needed, in order to fill in the gaps and coherently reformulate the strategy, for a successful implementation.
Image source:

Tags: Ask the Experts, Performance Management, Strategy Map